Webinar Replay - Possible Workflows to Simulate Tailings Planning using Muk3D
- Simon
- Apr 4, 2025
- 5 min read
This is the replay from the 26 of March 2025 webinar where we explored six workflows available in Muk3D to simulate tailings planning.
Tailings planning involves designing, constructing, operating, and closing tailings storage facilities (TSFs) over the complete life of a project. According to ANCOLD guidelines, a Tailings Management Plan (TMP) should be flexible and can be generally subdivided into broad categories Short, Medium, and Long-Term plans, addressing the evolving requirements as the mine progresses.
From a geometric modelling perspective, Short, Medium, and Long-Term Plans each serve different levels of detail and time horizons:
Long-Term Plan: Ensures overall capacity for the life of the project (including possible extensions) and links to closure requirements.
Medium-Term Plan: Focuses on 3–5 year schedules, budgeting for construction, and aligning with the long-term strategy.
Short-Term Plan: Manages monthly or seasonal operations—such as tailings beach placement and water management—within the broader goals.
In Muk3D, these horizons are used to:
Model the TSF’s geometry and capacity expansions (long-term).
Schedule intermediate raises and plan for capital expenditures (medium-term).
Adjust daily/weekly operations and deposition strategies (short-term).
This tiered approach helps ensure that each stage of tailings management—from immediate operations to final closure—remains consistent with both near-term needs and long-term objectives.
Muk3D provides a suite of tools to simulate and model these stages of a TSF’s life. This note introduces 6 different workflows in Muk3D that can help you plan your tailings storage, each with its own strengths, limitations, and recommended applications.
Disclaimer: These workflows are examples of how one might use Muk3D for tailings planning. They are not the “holy grail” or definitive approach. In practice, you may mix and match or adapt these methods to your specific needs. Always verify that the chosen workflow and resulting model outputs are appropriate for your site conditions and project requirements.
Overview of 6 Muk3D Tailings Planning Workflows
These six workflows illustrate different levels of automation, complexity, and integration. The choice depends on your project requirements, data availability, technical skill set, and time constraints.
Remember that each approach—especially the automated ones—still needs thorough verification to ensure results are consistent with real-world conditions and meet regulatory requirements.
Below is a concise comparison of the six workflows:
Manual
Automated Sequencing Commands
Auto-Staging,
Tailings Storage Elevation Curves,
Scripting
Muk3D Simulation
Muk3D Simulation (Excel)
Muk3D Simulation (GoldSim)
Detailed Descriptions and Schematic Workflows
Below are simplified schematics to illustrate how each workflow might look in practice.
Manual Workflow
You perform every step manually, from creating a new project folder for each run, to deciding when and how to raise the walls, and manually depositing tailings.
When to Use: Ideal for learning, testing small or one-off designs, or verifying detailed, complex dam configurations.
Why: Gives you full control and an in-depth understanding of each step.
Advantages:
Complete control over geometry changes and sequencing.
Suited for complex or unusual designs requiring careful, step-by-step manipulation.
Disadvantages:
Labor-intensive and time-consuming.
High potential for human error (repetitive data entry).
Not scalable for multiple scenarios or repeated analyses.

Automated Sequencing Commands
These are methods that automate the sequencing of planning operations directly from within Muk3D.
Auto-Staging automate the raising of dam wall and filling the dam with tailings
Tailings Elevation Storage Curves automate the deposition of tailings with elevation
Auto-Staging
Muk3D automatically raises the dam to a predefined elevation and deposits tailings in a uniform manner.
When to Use: Good for mid to long-term planning where the design is relatively detailed deposition is not required. Can also be used ring dykes (incl. cycloned tails if you use small increment).
Why: Automates the process of raising the dam to certain elevations, quickly producing results for standard cases.
Advantages:
- Rapid updates of dam elevations.
- Simple to set up for ring dyke or single-stream deposition.
Disadvantages:
- Assumes uniform deposition around the perimeter.
- Limited ability to customize pond or deposition geometry.
- Not ideal for complex or multi-stream scenarios.
Tailings Storage Elevation Curves
Generates a quick volume-versus-elevation relationship for tailings, focusing on the filling of the TSF rather than the construction details.
When to Use: Useful for shorter-term planning or simpler TSFs (e.g., downstream construction) where volume estimates and quick filling sequences are needed.
Why: Provides a fast way to assess how tailings fill up to certain elevations without detailed wall-raising steps.
Advantages:
Quick generation of volume vs. elevation curves.
Straightforward for basic, single-stream scenarios.
Disadvantages:
No wall raising included in the workflow.
Deposition around the perimeter only; limited pond control.
Not suitable for multi-stream or complex designs.
Scripting
You write or record macros (Python or Muk3D’s macro system) to automate repetitive commands, reducing manual effort and error.
When to Use: Best for projects requiring repeated runs, scenario analyses, or systematic iteration without needing external programs.
Why: Reduces manual input and potential errors by automating sequences of Muk3D commands.
Advantages:
Highly systematic; once set up, it can be re-run with different inputs quickly.
Reduces the risk of human error compared to purely manual methods.
Disadvantages:
Requires familiarity with scripting.
Setting up scripts can be time-consuming.
Must validate the logic of the script to ensure correct outputs.

Muk3D Simulation Add-On
Muk3D Simulation (Excel)
Muk3D is connected to Excel so that inputs and outputs can be passed back and forth, enabling scenario control and quick data updates in a familiar spreadsheet environment.
When to Use: Ideal for more advanced scenario modeling where you want to manage data inputs (e.g., monthly production, pond levels) in Excel.
Why: Allows you to combine Muk3D’s spatial modeling with Excel’s data handling and calculations, automating the workflow without requiring more specialized software.
Advantages:
Comprehensive scenario management within Excel.
Automated data exchange between Muk3D and spreadsheets.
Faster to set up than GoldSim for many use cases.
Disadvantages:
Requires coding expertise and careful linkage between Excel and Muk3D.
Must validate data transfers thoroughly.
Limited to the capabilities of Excel for advanced analytics.

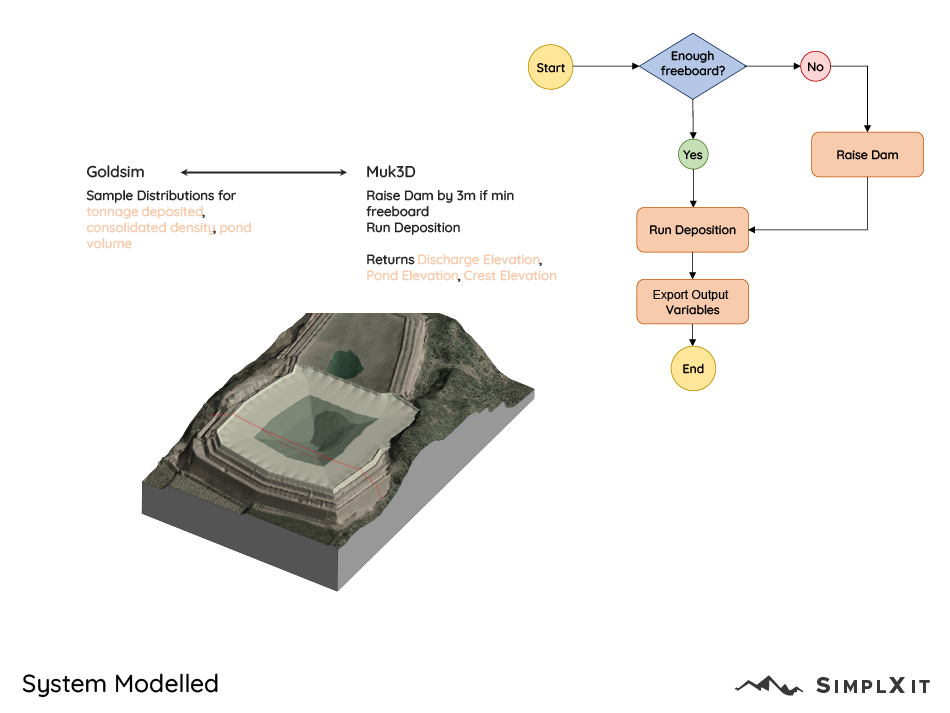
Muk3D Simulation (GoldSim)
Muk3D is connected to GoldSim, a powerful dynamic simulation and probabilistic modeling software. This allows for complex scenario analyses, uncertainty modeling, and advanced time-based simulations.
When to Use: Perfect for advanced scenario modeling where you need to integrate real-time production data, perform probabilistic/Monte Carlo simulations, or manage multiple process streams.
Why: Connects Muk3D directly with GoldSim to iterate through numerous scenarios, dynamically adjusting inputs based on external models.
Advantages:
Dynamic and probabilistic modeling for scenario analysis.
Automated data exchange between Muk3D and GoldSim.
Ideal for research-oriented or highly complex TSF designs.
Disadvantages:
Requires coding expertise and more complex setup.
Longer implementation time.
Must carefully validate data transfers and model logic.
References:
- Muk3D Knowledge Base and integrated User Manual
This post was prepared as a supporting document for a webinar demonstrating these six workflows for tailings planning using Muk3D. It is not a substitute for professional engineering judgment or site-specific risk assessments. Always consult qualified professionals and local regulatory guidelines when designing and operating tailings storage facilities.
Comments